Development of the atomic model worksheet – Embark on a captivating journey through the evolution of atomic models with our comprehensive worksheet. This meticulously crafted guide unveils the groundbreaking discoveries that shaped our understanding of the atom, providing a profound exploration of its structure, components, and applications.
Prepare to delve into the intricacies of atomic orbitals, unravel the secrets of electron configurations, and witness the remarkable periodic trends that govern the chemical world. Immerse yourself in a world of scientific exploration and gain an unparalleled understanding of the fundamental building blocks of matter.
Historical Timeline of Atomic Model Development
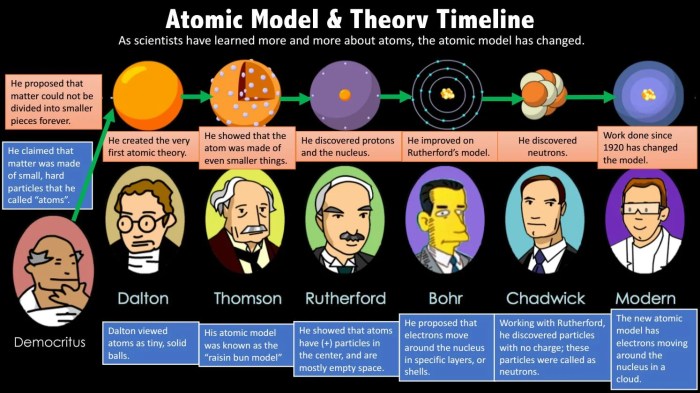
The development of the atomic model has been a gradual process, with significant contributions from numerous scientists over centuries. This timeline highlights key milestones and discoveries that have shaped our understanding of the atom:
- 400 BC:Democritus proposes the concept of atoms as indivisible particles.
- 1803:John Dalton’s atomic theory introduces the idea of atoms as spherical, indivisible particles with different masses.
- 1897:J.J. Thomson discovers the electron, leading to the “plum pudding” model of the atom.
- 1911:Ernest Rutherford’s gold foil experiment reveals the existence of a dense nucleus and positively charged particles (protons).
- 1913:Niels Bohr proposes the planetary model of the atom, with electrons orbiting the nucleus in specific energy levels.
- 1924:Louis de Broglie proposes the wave-particle duality of electrons.
- 1926:Erwin Schrödinger develops the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which describes electrons as waves and introduces the concept of orbitals.
- 1932:James Chadwick discovers the neutron, completing the understanding of the atom’s fundamental particles.
Key Scientists and Their Contributions: Development Of The Atomic Model Worksheet
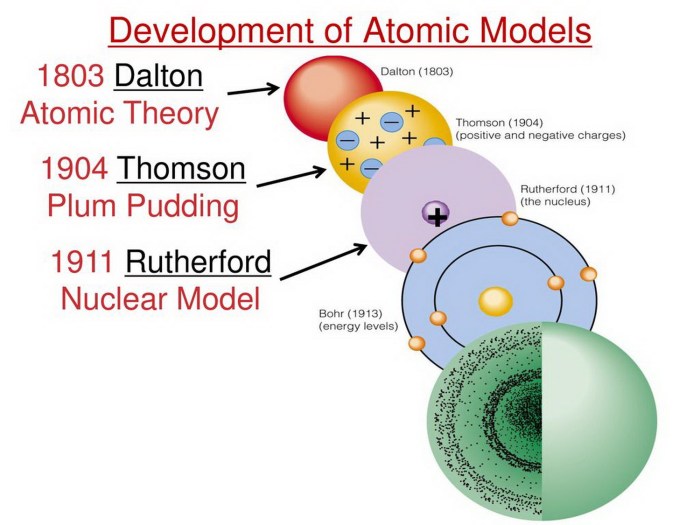
The development of the atomic model has been driven by the contributions of several brilliant scientists. Here are some key figures and their notable discoveries:
| Scientist | Contribution | Atomic Model |
|---|---|---|
| John Dalton | Proposed the atomic theory | Dalton’s atomic model |
| J.J. Thomson | Discovered the electron | Plum pudding model |
| Ernest Rutherford | Discovered the nucleus and protons | Rutherford’s model |
| Niels Bohr | Proposed the planetary model | Bohr’s model |
| Erwin Schrödinger | Developed the quantum mechanical model | Quantum mechanical model |
| James Chadwick | Discovered the neutron | Modern atomic model |
Structure and Components of the Atom
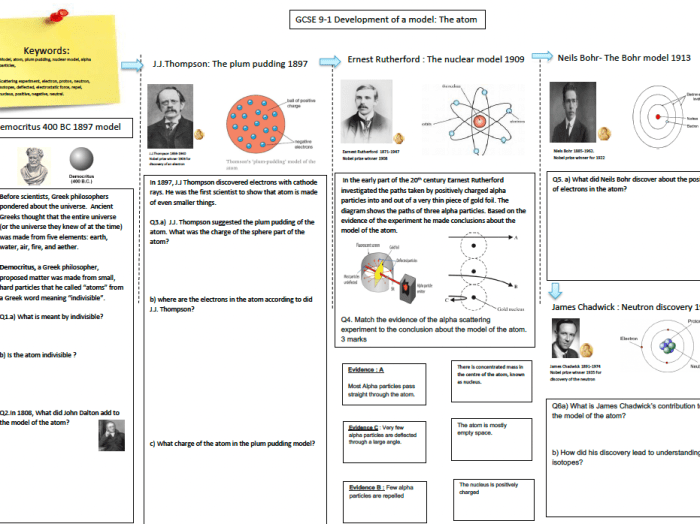
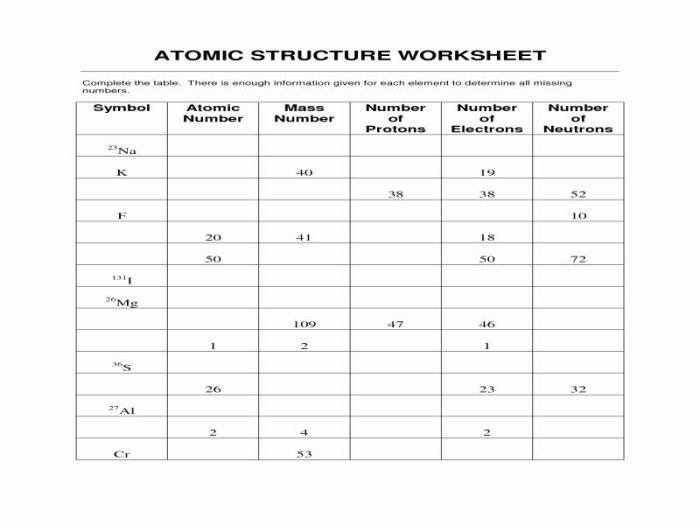
An atom consists of a central nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus contains protons, which are positively charged, and neutrons, which are neutral. Electrons are negatively charged and occupy specific energy levels around the nucleus.
- Nucleus:The dense, central core of the atom, containing protons and neutrons.
- Protons:Positively charged particles found in the nucleus.
- Neutrons:Neutral particles found in the nucleus.
- Electrons:Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels.
FAQ Overview
What are the key milestones in the development of the atomic model?
The key milestones include Dalton’s atomic theory, Thomson’s discovery of the electron, Rutherford’s discovery of the nucleus, Bohr’s planetary model, and the quantum mechanical model.
Who are the major scientists who contributed to the development of the atomic model?
The major scientists include John Dalton, J.J. Thomson, Ernest Rutherford, Niels Bohr, and Erwin Schrödinger.
What are the different components of an atom?
The components of an atom include the nucleus, electrons, and energy levels.
What is the significance of atomic orbitals?
Atomic orbitals describe the three-dimensional space around the nucleus where electrons are most likely to be found.
How do periodic trends help us understand the properties of elements?
Periodic trends allow us to predict the properties of elements based on their position in the periodic table, providing insights into their chemical reactivity and physical characteristics.